Stroke prevention therapy in atrial fibrillation patients
Uit Stolling en Antistolling
Inhoud
- 1 Stroke prevention atrial fibrillation patients
- 2 Oral anticoagulation in atrial fibrillation patients with chronic kidney disease
- 3 Recommendations for stroke prevention in patients with atrial fibrillation
- 4 Anticoagulation after a stroke
- 5 Recommendations for secondary stroke prevention
- 6 Initiation anticoagualtion after an intracranial bleed
- 7 Recommendations for combination therapy with oral anticoagulants and antiplatelets
- 8 Antithrombotic therapy after an ACS in AF patients requiring anticoagulation
- 9 Anticoagulation: before, during, and after ablation
Stroke prevention atrial fibrillation patients
Oral anticoagulation in atrial fibrillation patients with chronic kidney disease
Recommendations for stroke prevention in patients with atrial fibrillation
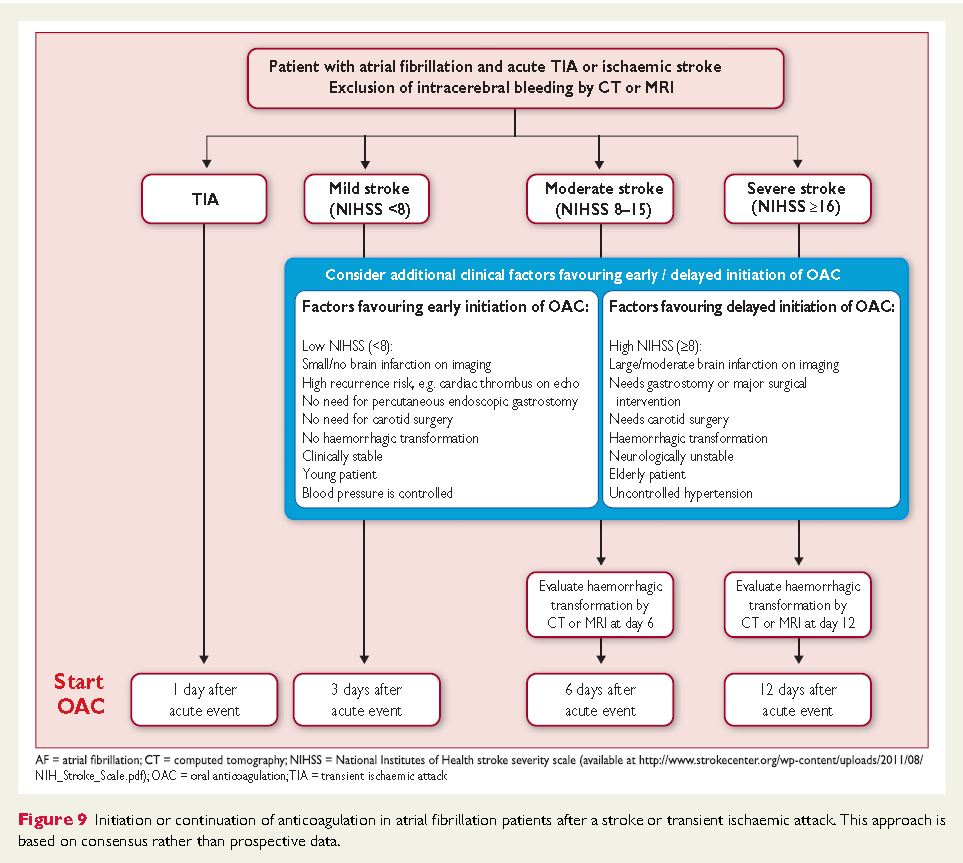
Anticoagulation after a stroke
Recommendations for secondary stroke prevention
Initiation anticoagualtion after an intracranial bleed
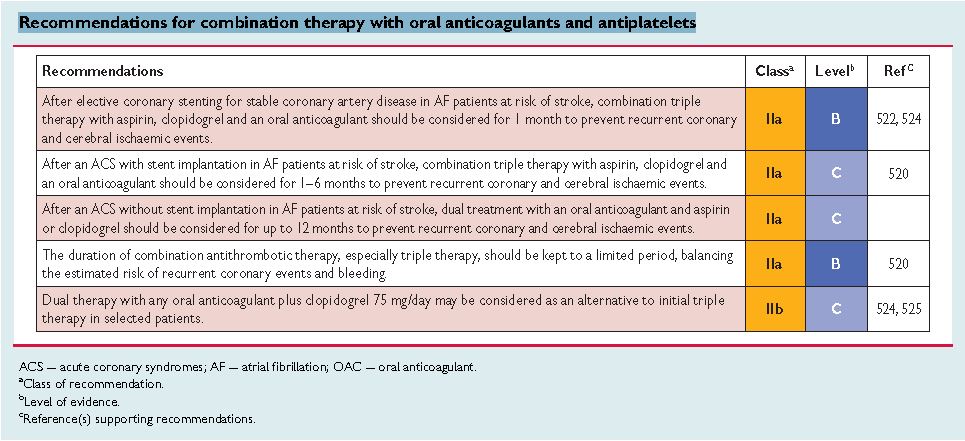
Recommendations for combination therapy with oral anticoagulants and antiplatelets
Antithrombotic therapy after an ACS in AF patients requiring anticoagulation
Anticoagulation: before, during, and after ablation
Patients anticoagulated with VKAs should continue therapy during ablation (with an INR of 2–3). Anticoagulation with NOACs is an alternative to warfarin. Anticoagulation should be maintained for at least 8 weeks after ablation for all patients. OAC after catheter ablation should follow general anticoagulation recommendations, regardless of the presumed rhythm outcome.